Shellbags
UsrClass.dat
Investigating Shellbags
Microsoft Windows tracks and records user’s view settings and preferences while exploring folders. These view settings (size, view mode, position) of a folder window are stored in Shellbags registry keys. Shellbags keep track of the view settings of a folder window once the folder has been viewed through Windows Explorer. Shellbags does not only track the view settings of a folder on the local machine, but also on removable devices and network folders.
Digital Forensics Value of Shellbags Artifacts
While the size, position and other view settings of a given folder window is not necessarily of a forensic value, Shellbags artifacts can provide valuable insights such as folders previously accessed/viewed on the local machine, network folders, and removable devices. As the existence of Shellbags information indicates that a specific folder(s) has been visited by the user; Windows Explorer will only create Shellbags information if the folder was initially viewed by the user. Shellbags keeps track of the view settings of a folder even if it was deleted or no longer exist on the system (folders located on a removable device such as external hard drives or USB flash drives), which means that we can retrieve information about previously existing folders. Windows Shellbags also provides information about when a particular folder was created, last accessed, and last modified. This type of information is of forensic value as it can help investigators in understanding and reconstructing previous events on a particular device.
Location of Shellbags Artifacts
The location for Shellbags artifacts differs slightly between Windows operating systems. For Windows XP, Shellbags artifacts are stored in NTUSER.DAT registry hive in the following registry keys:
Windows XP
NTUSER.DAT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Shell
NTUSER.DAT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\ShellNoRoam
NTUSER.DAT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\StreamMRU
Windows 7,8, 8.1 and 10 Similarly, the later versions of Windows store Shellbags information in NTUSER.DAT registry hive. Unlike Windows XP, however, Shellbags artifacts are only stored under the Shell Key.
NTUSER.DAT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\BagMRU
NTUSER.DAT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\Bags
Shellbags artifacts are also found in UsrClass.dat hive at the following locations:
USRCLASS.DAT\Local Settings\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\BagMRU
USRCLASS.DAT\Local Settings\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\Bags
Structure of Shellbags Artifacts
Shellbags structure is slightly different between Windows operating systems. However, Shellbags artifacts are contained in two main registry keys, BagMRU and Bags.
BagMRU key:
BagMRU key consists of multiple numbered subkeys. These subkeys represent the actual directory structures of folders that have been accessed through Windows Explorer. The BagMRU key itself represents the Desktop; however, the rest of the subkeys are not assigned to a specific folder but rather structured to the hierarchy in which folders were accessed. Each of these numbered subkeys, including the BagMRU key, contains the following values:
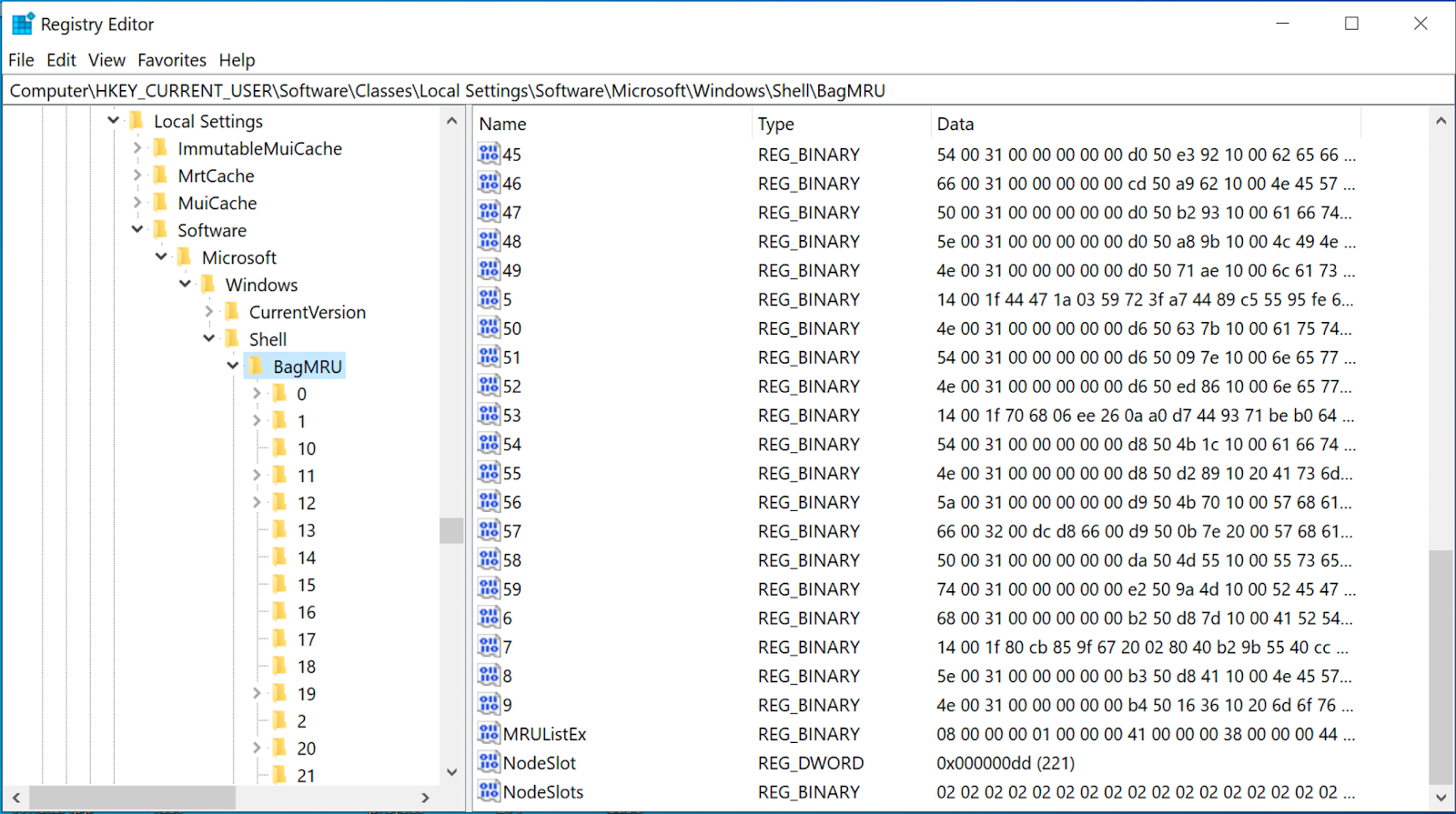
MRUListEx: this value indicates the order in which each child folder within the current key was last accessed.
NodeSlot: this value corresponds to the Bags key which contains the view settings for that specific folder.
NodeSlots: this value is only located in BagMRU key and it is updated upon new Shellbag creation.
Bags key: The Bags key also consists of multiple numbered subkeys; however, each of the subkeys within Bags key stores the view settings (view mode, size, location) of the child subkeys under BagMRU key.
Shellbags Artifact
This artifact contains information extracted from Shellbags registry keys. The details you can view include:
Value – Indicates the folder name.
Absolute Path – The absolute path to the folder.
Bag Path – The bag path.
MFT Entry Number – The MFT entry number of the folder.
MFT Sequence number – The MFT sequence number of the folder.
In addition, it contains multiple important timestamps including:
Creation Date – The date/time when the folder was created.
Last Access – The date/time when the folder was last accessed.
Last Modification Date – The date/time when the folder was last modified.
Last updated